薬生薬審発0202第1号(平成29年2月2日)
ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE- M4E(R2) – Dated 15 June 2016
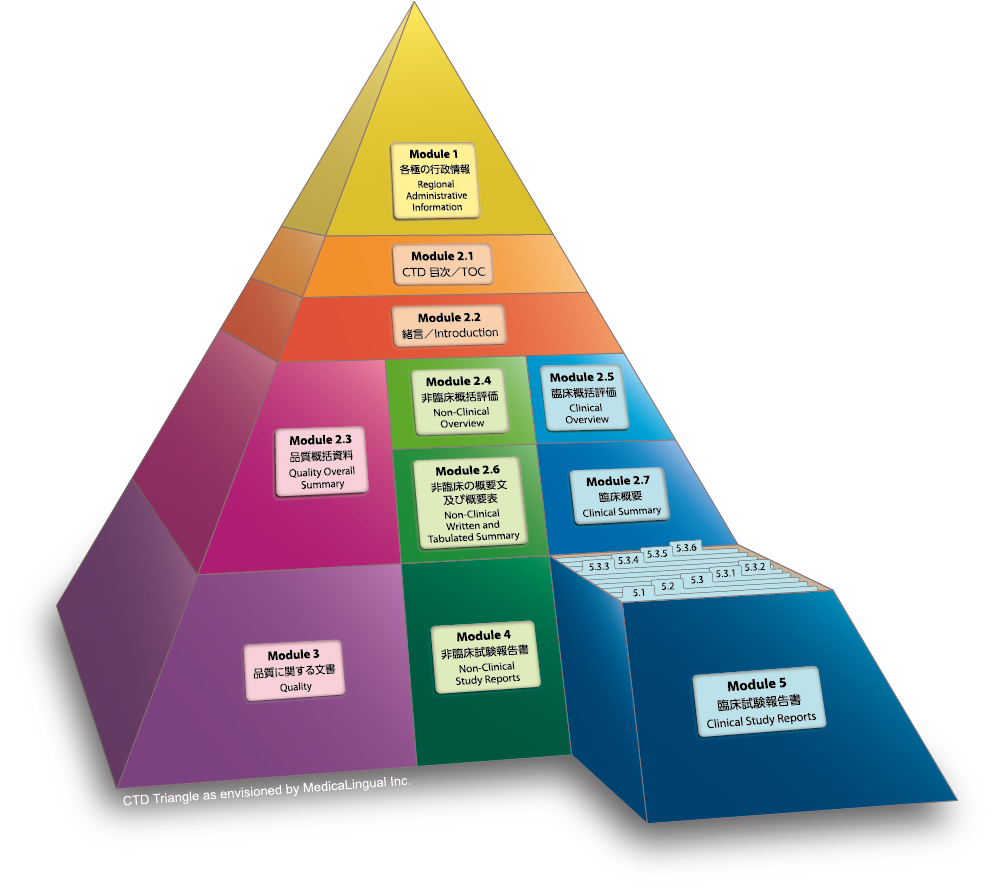
Module 5 臨床試験報告書
5.3 試験報告書及び関連情報
5.3.3 臨床薬物動態(PK)試験報告書
健康被験者、患者におけるPK特性の評価は、投与計画及び用量調整の検討や、併用薬剤による影響の予測、観察された薬力学的作用の差異を解釈する上で重要である。PK評価は、親化合物及び代謝物(特に薬理活性がある場合)が、生体内でどのような挙動を示すかを経時的に検討するものであり、最高血漿中濃度(最大曝露量)、AUC(総曝露量)、クリアランス、そして蓄積に焦点が置かれるものである。
Module 5 CLINICAL STUDY REPORTS
5.3 Clinical Study Reports
5.3.3 Reports of Human Pharmacokinetic (PK) Studies
Assessment of the PK of a drug in healthy subjects and/or patients is considered critical to designing dosing strategies and titration steps, to anticipating the effects of concomitant drug use, and to interpreting observed pharmacodynamic differences. These assessments should provide a description of the body’s handling of a drug over time, focusing on maximum plasma concentrations (peak exposure), area-under-curve (total exposure), clearance, and accumulation of the parent drug and its metabolite(s), in particular those that have pharmacological activity.
第5.3.3.1項及び第5.3.3.2項の対象となるPK試験の目的としては、(1)血漿中薬物及び代謝物濃度の経時的測定、(2)有用又は必要な場合には尿中又は糞中の薬物及び代謝物濃度の測定、(3)蛋白質や赤血球と結合した薬物及び代謝物の測定等が一般的である。
The PK studies whose reports should be included in Sections 5.3.3.1 and 5.3.3.2 are generally designed to (1) measure plasma drug and metabolite concentrations over time, (2) measure drug and metabolite concentrations in urine or faeces when useful or necessary, and/or (3) measure drug and metabolite binding to protein or red blood cells.
PK試験には、組織、臓器、体液(例:滑液や脳脊髄液)への薬物分布測定が含まれる場合もあるが、その結果は第5.3.3.1項又は第5.3.3.2項に適切に添付すること。これらの試験により、薬物のPK特性を明らかにするとともに、健康被験者、患者における薬物及び活性代謝物の吸収・分布・代謝・排泄に関する情報を提供すること。マスバランス試験や、用量(例:用量比例性)や時間(例:酵素誘導又は抗体産生の影響)と関連したPKの変化を検討した試験は特に重要であり、結果は第5.3.3.1項又は第5.3.3.2項に添付すること。健康志願者及び患者におけるPKの測定結果は、平均値による記述とは別に、個々の変動範囲についても記述すること。外国臨床データを受け入れる際に考慮すべき民族的要因に関するICH E5ガイドラインでは、異なる集団における異なる薬物反応をもたらす要因として内因性民族的要因と外因性民族的要因を挙げている。本ガイドラインでは、これらの分類をそれぞれ内因性要因及び外因性要因と記述する。これら内因性要因(例:年齢、性、人種、体重、身長、疾患、遺伝子多型及び臓器機能不全)及び外因性要因(例:薬物間相互作用、食事、喫煙及び飲酒)によるPKの変化の結果としての全身曝露量の違いを評価することもある。これら内因性及び外因性要因の影響を検討した試験報告書は、第5.3.3.3項及び第5.3.3.4項にそれぞれ添付すること。
On occasion, PK studies may include measurement of drug distribution into other body tissues, body organs, or fluids (e.g., synovial fluid or cerebrospinal fluid), and the results of these tissue distribution studies should be included in Section 5.3.3.1 to 5.3.3.2, as appropriate. These studies should characterise the drug’s PK and provide information about the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of a drug and any active metabolites in healthy subjects and/or patients. Studies of mass balance and changes in PK related to dose (e.g., determination of dose proportionality) or time (e.g., due to enzyme induction or formation of antibodies) are of particular interest and should be included in Sections 5.3.3.1 and/or 5.3.3.2. Apart from describing mean PK in normal and patient volunteers, PK studies should also describe the range of individual variability. In the ICH E5 guideline on Ethnic Factors in the Acceptance of Foreign Data, factors that may result in different responses to a drug in different populations are categorised as intrinsic ethnic factors or extrinsic ethnic factors. In this document, these categories are referred to as intrinsic factors and extrinsic factors, respectively. Additional studies can also assess differences in systemic exposure as a result of changes in PK due to intrinsic (e.g., age, gender, racial, weight, height, disease, genetic polymorphism, and organ dysfunction) and extrinsic (e.g., drug-drug interactions, diet, smoking, and alcohol use) factors. Reports of PK studies examining the influence of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on exposure should be organised in Sections 5.3.3.3 and 5.3.3.4, respectively.
繰返しサンプルを採取する標準的PK試験に加え、臨床試験において少数回サンプルを採取するポピュレーションPK解析によっても、用量-PK-反応関係の変化における内因性及び外因性要因の関与を検討することができる。ポピュレーションPK試験で用いられる方法は、標準的PK試験で用いられるものとは本質的に異なっているため、これらの試験報告書は第5.3.3.5項に添付すること。
In addition to standard multiple-sample PK studies, population PK analyses based on sparse sampling during clinical studies can also address questions about the contributions of intrinsic and extrinsic factors to the variability in the dose-PK-response relationship. Because the methods used in population PK studies are substantially different from those used in standard PK studies, these studies should be placed in Section 5.3.3.5.
5.3.3.1 健康被験者におけるPK及び初期忍容性試験報告書
健康被験者におけるPK及び初期忍容性試験の報告書は、本項に添付すること。
5.3.3.1 Healthy Subject PK and Initial Tolerability Study Reports
Reports of PK and initial tolerability studies in healthy subjects should be placed in this section.
5.3.3.2 患者におけるPK及び初期忍容性試験報告書
患者におけるPK及び初期忍容性試験の報告書は、本項に添付すること。
5.3.3.2 Patient PK and Initial Tolerability Study Reports
Reports of PK and initial tolerability studies in patients should be placed in this section.
5.3.3.3 内因性要因を検討したPK試験報告書
内因性要因を検討したPK試験報告書は、本項に添付すること。
5.3.3.3 Intrinsic Factor PK Study Reports
Reports of PK studies to assess effects of intrinsic factors, should be placed in this section.
5.3.3.4 外因性要因を検討したPK試験報告書
外因性要因を検討したPK試験報告書は、本項に添付すること。
5.3.3.4 Extrinsic Factor PK Study Reports
Reports of PK studies to assess effects of extrinsic factors, should be placed in this section.
5.3.3.5 ポピュレーションPK試験報告書
有効性及び安全性試験を含む臨床試験で少数回採取したサンプルに基づくポピュレーションPK試験の報告書は、本項に添付すること。
5.3.3.5 Population PK Study Reports
Reports of population PK studies based on sparse samples obtained in clinical trials including efficacy and safety trials, should be placed in this section.