治験の統括報告書の構成と内容に関するガイドライン
平成8年5月1日 薬審第335号
各都道府県衛生主管部(局)長あて 厚生省薬務局審査課長通知
STRUCTURE AND CONTENT OF CLINICAL STUDY REPORTS
Recommended for Adoption at Step 4 of the ICH Process on 30 November 1995 by the ICH Steering Committee
序文
本ガイドラインは,治験の総括報告書の作成に当たっての,その構成と内容に関する指針を示すものである。本ガイドラインは,ICH ガイドライン“Structure and Content of Clinical Study Report”に基づいて作成されたものであり,本ガイドラインに基づいて作成された総括報告書の中核部分は,ICH 参加地域の全ての審査当局に共通に受け入れ可能となる。個々の審査当局が特別に必要とする資料は,要求に応じてこの中核部分に添付する付録として構成される。
INTRODUCTION TO THE GUIDELINE
The objective of this guideline is to allow the compilation of a single core clinical study report acceptable to all regulatory authorities of the ICH regions. The regulatory authority specific additions will consist of modules to be considered as appendices, available upon request according to regional regulatory requirements.
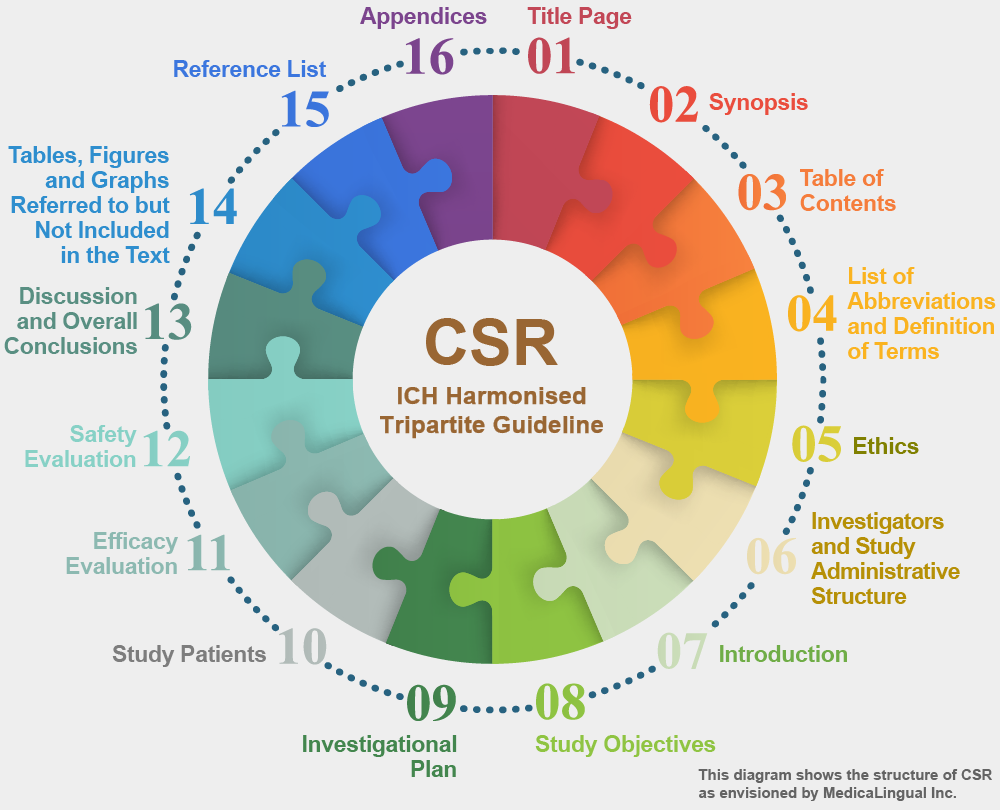
本ガイドラインに記載された治験の総括報告書は,患者を対象として実施された治療薬,予防薬又は診断薬(以下,薬剤又は治療と略す)の個々の治験についての臨床及び統計上の記述,提示及び分析内容を一つの報告書に統合した「統合された」詳細報告書である。報告書には,表及び図を報告書本文中か本文の末尾に含め,付録には,治験実施計画書,症例記録用紙の見本,治験責任医師(治験実施施設において治験の実施に関して責任を有する医師又は歯科医師)等に関する情報,治験薬(被験薬又は対照薬として用いられる有効成分を含む製剤又はプラセボ)に関する情報,技術的統計的文書,関連する刊行物,患者データの一覧表,並びに計算式の導出,コンピュータ処理,分析及びコンピュータ出力などの技術的統計的な詳細に関する事項を含めること。別々の臨床及び統計報告書を単に合わせたものをもって,治験の統合された詳細報告書とすべきではない。本ガイドラインは,有効性及び安全性の評価を目的とした治験を主な対象としているが,ここに述べる基本的原則及び構成は,例えば臨床薬理試験のような他の種類の治験にも適用が可能である。試験の性質と重要性によっては,簡略化された報告書が適切であることもある。
The clinical study report described in this guideline is an “integrated” full report of an individual study of any therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic agent (referred to herein as drug or treatment) conducted in patients, in which the clinical and statistical description, presentations, and analyses are integrated into a single report, incorporating tables and figures into the main text of the report, or at the end of the text, and with appendices containing the protocol, sample case report forms, investigator related information, information related to the test drugs/investigational products including active control/comparators, technical statistical documentation, related publications, patient data listings, and technical statistical details such as derivations, computations, analyses, and computer output etc. The integrated full report of a study should not be derived by simply joining a separate clinical and statistical report. Although this guideline is mainly aimed at efficacy and safety trials, the basic principles and structure described can be applied to other kinds of trials, such as clinical pharmacology studies. Depending on the nature and importance of such studies, a less detailed report might be appropriate.
本ガイドラインは,完備していて,不明瞭な点がなく,きちんと整理され,かつ審査が容易な報告書の作成のために,治験依頼者を支援することを目的としている。報告書には,治験の主要なデザイン上の特徴がどのように選択されたかを明確に説明し,さらに治験の計画,方法及び実施について十分な情報を含めること。それにより,治験の実施方法に関する不明瞭な点がなくなる。報告書には,付録を含めて,人口統計学的データ及び基準値を含む十分な個別患者データ並びに解析方法の詳細を提示すること。それにより,審査当局が望むときには,特に重要な解析をやり直すことも可能になる。さらに,全ての解析,表及び図に関しては,それらがどの患者集団をもとに作られたかが明確に同定できる情報を本文中又は図表の一部分に含むことが重要である。
The guideline is intended to assist sponsors in the development of a report that is complete, free from ambiguity, well organised and easy to review. The report should provide a clear explanation of how the critical design features of the study were chosen and enough information on the plan, methods and conduct of the study so that there is no ambiguity in how the study was carried out. The report with its appendices should also provide enough individual patient data, including the demographic and baseline data, and details of analytical methods, to allow replication of the critical analyses when authorities wish to do so. It is also particularly important that all analyses, tables, and figures carry, in text or as part of the table, clear identification of the set of patients from which they were generated.
例えば対照を置かない試験又は有効性を立証できるようにデザインされていない試験(しかし安全性に関する比較対照試験については完全な報告書を作成すること),重大な不備のある若しくは中断された試験,又は申請効能となる病態とは明らかに無関係な病態に対する比較対照試験などの場合には,要約したデータを用いたり,いくつかの章を削除した簡略化された報告書が受け入れ可能であろう。しかし,このような場合でも,安全性の側面については詳細な記述を含めること。簡略化された報告書を提出する場合には,デザイン及び結果についての詳細を十分に示すことにより,審査当局が詳細な報告書が必要かどうかを判断できるようにすること。詳細な報告書が必要かどうかについて疑問があれば,審査当局に相談することが役立つであろう。
Depending on the regulatory authority’s review policy, abbreviated reports using summarised data or with some sections deleted, may be acceptable for uncontrolled studies or other studies not designed to establish efficacy (but a controlled safety study should be reported in full), for seriously flawed or aborted studies, or for controlled studies that examine conditions clearly unrelated to those for which a claim is made. However, a full description of safety aspects should be included in these cases. If an abbreviated report is submitted, there should be enough detail of design and results to allow the regulatory authority to determine whether a full report is needed. If there is any question regarding whether the reports are needed, it may be useful to consult the regulatory authority.
治験の実施方法の詳細な説明としては,最初の治験実施計画書の記述を単に繰り返し述べることでよい場合もある。しかしながら,別の文書でより簡潔に試験方法を示すことが可能であることが多い。治験のデザイン及び実施について記述しているそれぞれの章では,治験実施計画書には十分に記述されていない試験の特徴を明らかにしたり,実際に実施された方法のうちどこが治験実施計画書と異なっていたかを明確にすることや,計画された治験実施計画書からの逸脱を吟味するために用いた統計手法や分析について考察することが特に重要である。
In presenting the detailed description of how the study was carried out, it may be possible simply to restate the description in the initial protocol. Often, however, it is possible to present the methodology of the study more concisely in a separate document. In each section describing the design and conduct of the study, it is particularly important to clarify features of the study that are not well-described in the protocol and identify ways in which the study as conducted differed from the protocol, and to discuss the statistical methods and analyses used to account for these deviations from the planned protocol.
個々の治験の十分に統合された総括報告書には,個々の有害事象や臨床検査値異常に関する最も詳細な考察を含めること。しかし,通常これらは,どのような申請書類においても,利用可能な全てのデータを対象とする総括的な安全性の分析のなかで再吟味されるべきである。
The full integrated report of the individual study should include the most detailed discussion of individual adverse events or laboratory abnormalities, but these should usually be reexamined as part of an overall safety analysis of all available data in any application.
報告書には,治験対象集団の人口統計学的特性(demographic characteristics)及びその他の予後に影響し得る因子を記述すること。さらに,治験が十分に大規模であって可能な場合には,人口統計学的な(例えば,年齢,性,人種,体重の)部分集団や,その他(例えば,腎機能や肝機能)の部分集団に関するデータを示すこと。それにより,有効性又は安全性に存在し得る差異を明確にすることができる。しかしながら,通常は,総括的な分析に用いられるさらに大きなデータベースにおいて,部分集団の反応は吟味されるべきである。
The report should describe demographic and other potentially predictive characteristics of the study population and, where the study is large enough to permit this, present data for demographic (e.g., age, sex, race, weight) and other (e.g., renal or hepatic function) subgroups so that possible differences in efficacy or safety can be identified. Usually, however, subgroup responses should be examined in the larger database used in the overall analysis.
報告書の一部として要求されるデータ一覧表(通常は付録に含まれる)は,主要な解析の裏付けに必要なものである。報告書の一部としてのデータ一覧表は,審査官がすぐに使用可能なものとすること。したがって,限られた大きさの一つの表に多くの変数を含めることが望ましい場合もあるが,そのために明瞭さを犠牲にしないこと。データが多いからといって,単語又は理解しやすい略号の代わりに記号を過剰に用いたり,表示を細かくし過ぎたりしないこと。このような場合には,複数の一覧表を作ることが望ましい。
The data listings requested as part of the report (usually in an appendix) are those needed to support critical analyses. Data listings that are part of the report should be readily usable by the reviewer.
Thus, although it may be desirable to include many variables in a single listing to limit size, this should not be at the expense of clarity. An excess of data should not be allowed to lead to overuse of symbols instead of words or easily understood abbreviations or to too small displays etc. In this case, it is preferable to produce several listings.
報告書においては,データを様々な程度の詳細さで提示することが要求される。重要な人口統計学的変数,有効性及び安全性の変数に関して全体的に要約した図表は,重要な点を示すために本文中に含めてもよい。その他の人口統計学的変数,有効性及び安全性の変数に関する要約された図表及び一覧表は,本文末尾の14章に提示すること。特定の患者群の個人データは,一覧表として付録16.2に添付すること。
Data should be presented in the report at different levels of detail: overall summary figures and tables for important demographic, efficacy and safety variables may be placed in the text to illustrate important points; other summary figures, tables and listings for demographic, efficacy and safety variables should be provided in section 14; individual patient data for specified groups of patients should be provided as listings in Appendix 16.2; and all individual patient data (archival listings requested only in the US) should be provided in Appendix 16.4.
いかなる図表やデータ一覧表においても,推定値又は計算により求めた値が使われたならば,それと分かるように明示すること。どのような方法でその値を推定又は計算したか,またどんな仮定に基づいているのかについて詳細な説明を示すこと。
In any table, figure or data listing, estimated or derived values, if used, should be identified in a conspicuous fashion. Detailed explanations should be provided as to how such values were estimated or derived and what underlying assumptions were made.
以下に示した指針は詳細なものであり,申請後のデータの説明や解析の追加要求を可能な限り少なくできるように,通常提出されるべき情報が何であるかを申請者に示すことを目的としている。しかしながら,データの提示及び(又は)解析に関する個々の要求事項は,時代,薬効群,地域等の状況に左右される場合があり,一般的な形式には記述できない。それ故,可能な限り個別の臨床ガイドラインを参照したり,データの提示及び解析について審査当局と協議することが重要である。
The guidance provided below is detailed and is intended to notify the applicant of virtually all of the information that should routinely be provided so that post-submission requests for further data clarification and analyses can be reduced as much as possible. Nonetheless, specific requirements for data presentation and/ or analysis may depend on specific situations, may evolve over time, may vary from drug class to drug class, may differ among regions and cannot be described in general terms; it is therefore important to refer to specific clinical guidelines and to discuss data presentation and analyses with the reviewing authority, whenever possible. Detailed written guidance on statistical approaches is available from some authorities.
どの報告書においても,ここに記載された全ての事項を(明らかに無関係でない限り)考慮すること。ある特定の治験において,別の方法がより論理的な場合には,事項の個々の順序や章分けを変えてもよい。
Each report should consider all of the topics described (unless clearly not relevant) although the specific sequence and grouping of topics may be changed if alternatives are more logical for a particular study. Some data in the appendices are specific requirements of individual regulatory authorities and should be submitted as appropriate. The numbering should then be adapted accordingly.
非常に大規模な治験の場合には,本ガイドラインの規定のいくつかが実際的でなかったり不適切であるかもしれない。そのような治験の計画時や報告時には,審査当局と連絡を取り,適切な報告書の書式について協議することが奨励される。
In the case of very large trials, some of the provisions of this guideline may be impractical or inappropriate. When planning and when reporting such trials, contact with regulatory authorities to discuss an appropriate report format is encouraged.
本ガイドラインの規定は,他のICH のガイドラインと関連づけて使用されたい。
The provisions of this guideline should be used in conjunction with other ICH guidelines.
ガイドラインQ&A
本ガイドラインの役割
Q1:治験における本ガイドラインの役割についてお示し願いたい。
A1:本ガイドラインは,治験の総括報告書の書き方のガイドラインであるが,結果の記載のみではなく,他に,治験の目的,計画,実施,解析,評価及び十分な個々の患者データなどの広範な内容が含まれる。
例えば,本ガイドラインの「治験の計画」の章には,治験デザインについての論点や,計画作成に当たり説明が必要となる事項が述べられており,本ガイドラインに則った総括報告書を作成するためには,治験計画作成時から,そのための注意が払われなければならない。また,本ガイドラインではデータの品質管理及び品質保証の方法の記載が求められており,そのためには,治験の実施にあたって品質管理および品質保証の実施が求められる。
治験の総括報告書の位置付け
Q2:治験の総括報告書の国際間での相互利用について伺いたい。
A2:本ガイドラインは,日,米,欧3極で相互に受入れ可能な治験の総括報告書の構成及び内容について定めたものである。これは文書としての要件を定めたもので,これに従って報告書を作成すれば,そのままその治験データが相互に受入れ可能であることを意味する訳ではない。外国で実施された臨床試験データの取扱いについては,ICH の場において検討がなされているところである。
また,外国語で作成された報告書を用いて,我が国で承認申請を行う場合は,従来の外国語で書かれた資料の取扱いと同様に,日本語訳を提出する必要がある。
***