薬生薬審発0202第1号(平成29年2月2日)
ICH HARMONISED GUIDELINE- M4E(R2) – Dated 15 June 2016
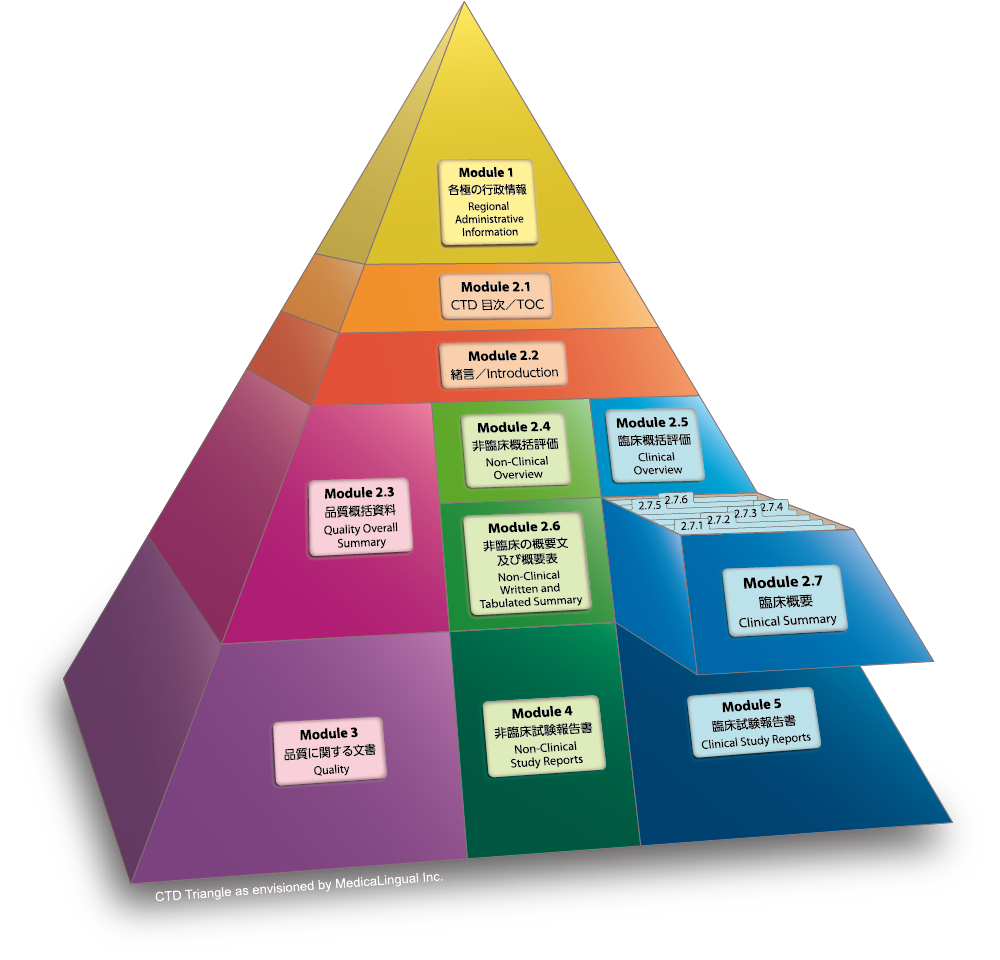
Module 2.7 臨床概要
2.7.2 臨床薬理の概要
2.7.2.1 背景及び概観
本項では、臨床薬理試験についての総括的な概要を示すこと。これらの試験には、ヒトでの薬物動態(PK)と薬力学(PD)を評価するための臨床試験、PKに関連するヒト細胞、組織、又は関連試料(以後、ヒト生体試料という)を用いて実施したin vitro試験が含まれる。ワクチン製品については、本項で投与量、投与スケジュール、最終製剤の選択を裏付ける免疫反応データを示すこと。適切な場合には、第2.7.1項、第2.7.3項、第2.7.4項で要約する関連データも参照して、薬物動態、薬力学、PK/PD、ヒト生体試料に関する情報の収集に用いた方法と根拠の包括的な概要を示してもよい。本項には個々の試験に関する詳細な情報を含めないこと。
Module 2.7 CLINICAL SUMMARY
2.7.2 Summary of Clinical Pharmacology Studies
2.7.2.1 Background and Overview
This section should provide the reviewer with an overall view of the clinical pharmacology studies. These studies include clinical studies performed to evaluate human pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD), and in vitro studies performed with human cells, tissues, or related materials (hereinafter referred to as human biomaterials) that are pertinent to PK processes. For vaccine products, this section should provide the reviewer with immune response data that support the selection of dose, dosage schedule, and formulation of the final product. Where appropriate, relevant data that are summarised in sections 2.7.1, 2.7.3 and 2.7.4 can also be referenced to provide a comprehensive view of the approach and rationale for the development of the pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, PK/PD and human biomaterial database. This section should not include detailed information about individual studies.
本項は、まず、PK又はPDデータの解釈を助けるために実施されたヒト生体試料試験の簡潔な概観から始めること。透過性(例:腸での吸収、血液脳関門通過)、タンパク結合、肝代謝、代謝に基づく薬物相互作用に関する試験は特に重要である。次に、健康被験者及び患者におけるPK/PD関係、PKとPK/PD関係に対する内因性及び外因性要因*1の重要な影響についての試験等、医薬品のPK及びPDの特性を明らかにするために実施された臨床試験の簡潔な概観を記載すること。試験デザイン及びデータ解析の重要な側面を記載すること(例:単回又は反復投与の選択、試験対象集団、検討した内因性及び外因性要因の選択、PDエンドポイントの選択、データを収集・解析してPK又はPDを評価するために標準的方法を用いたのか、あるいはポピュレーション法を用いたのか)。
*1 外国臨床データを受入れる際に考慮すべき民族的要因についてのICH E5ガイドラインでは、被験者集団間で異なる医薬品の反応を引き起こす可能性のある要因を内因性民族的要因と外因性民族的要因に分類している。CTDにおいては、これらの分類をそれぞれ内因性要因と外因性要因と呼ぶ。
This section should begin with a brief overview of the human biomaterial studies that were conducted and that were intended to help in the interpretation of PK or PD data. Studies of permeability (e.g., intestinal absorption, blood brain barrier passage), protein binding, hepatic metabolism, and metabolic-based drug-drug interactions are particularly relevant. This should be followed by a brief overview of the clinical studies that were carried out to characterise PK and PD of the medicinal product, including studies of PK/PD relationships in healthy subjects and patients, and relevant effects of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on PK and PK/PD relationships*. Critical aspects of study design and data analysis should be noted, e.g., the choice of the single or multiple doses used, the study population, choice of the intrinsic or extrinsic factors that were studied, the choice of PD endpoints, and whether a traditional approach or a population approach was used to collect and analyse data to assess PK or PD.
* In the ICH E5 guideline on Ethnic Factors in the Acceptance of Foreign Data, factors that may result in different responses to a drug in different populations are categorized as intrinsic ethnic factors or extrinsic ethnic factors. In this document, these categories are referred to as intrinsic factors and extrinsic factors, respectively.